Project Overview
The rising popularity of AI chatbots for mental health has led to increasing concerns about the lack of empathy in conversational AI agents. However, prior work on emotionally intelligent agents has focused on simulating human empathy, which has raised ethical concerns about deception and inauthenticity. In contrast, our work investigates how empathic human-AI interactions can benefit humans.
Approach
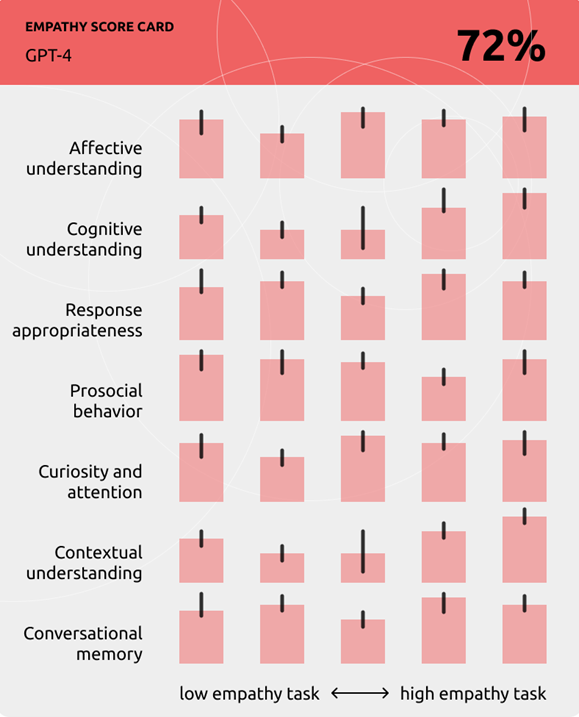
We proposed a multidimensional framework of perceived empathic behaviors that includes 7 dimensions that are inspired by theories of cognitive and affective empathy in psychology but reframed as interactional, behaviorally observable phenomenon in AI agents.
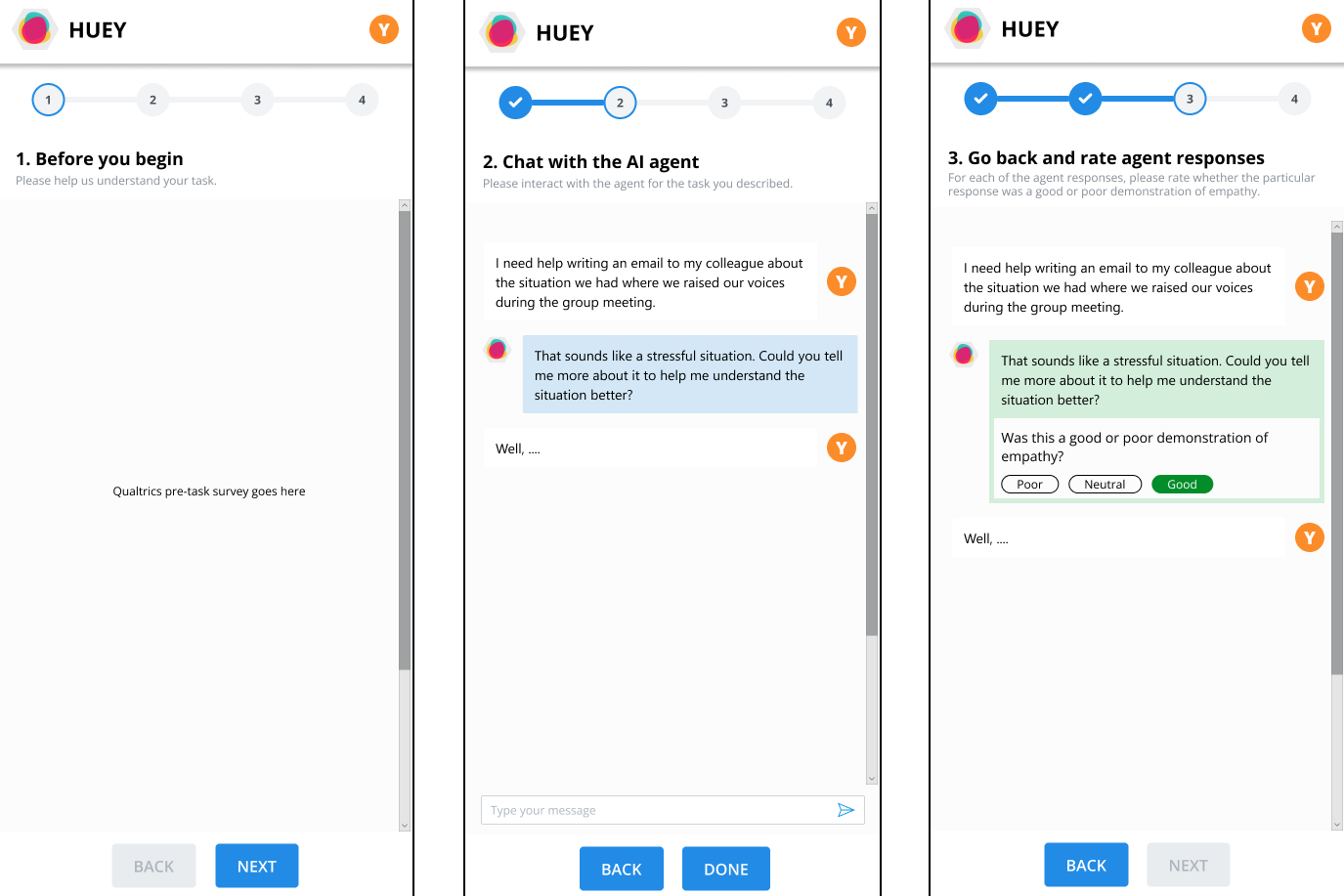
To understand how individual and contextual differences influence perceptions of empathy dimensions in various AI systems, we conducted a study with 151 participants who engaged with one out of 4 different AI agents and assessed their perception of empathic behaviors in that agent. From each conversation, we obtained first-person and per-turn labels of perceived empathic agent responses.
Outcomes
The main contributions of this work include our 7-dimensional digital empathy scale and an annotated dataset of empathic behaviors in conversational AI (Suh et al., 2025).
References
2025
-
SENSE-7: Taxonomy and Dataset for Measuring User Perceptions of Empathy in Sustained Human-AI Conversations
Jina Suh,
Lindy Le, Erfan Shayegani, Gonzalo Ramos, Judith Amores, Desmond C Ong, Mary Czerwinski, and Javier Hernandez
arXiv preprint arXiv:2509.16437, Sep 2025
Empathy is increasingly recognized as a key factor in human-AI communication, yet conventional approaches to "digital empathy" often focus on simulating internal, human-like emotional states while overlooking the inherently subjective, contextual, and relational facets of empathy as perceived by users. In this work, we propose a human-centered taxonomy that emphasizes observable empathic behaviors and introduce a new dataset, Sense-7, of real-world conversations between information workers and Large Language Models (LLMs), which includes per-turn empathy annotations directly from the users, along with user characteristics, and contextual details, offering a more user-grounded representation of empathy. Analysis of 695 conversations from 109 participants reveals that empathy judgments are highly individualized, context-sensitive, and vulnerable to disruption when conversational continuity fails or user expectations go unmet. To promote further research, we provide a subset of 672 anonymized conversation and provide exploratory classification analysis, showing that an LLM-based classifier can recognize 5 levels of empathy with an encouraging average Spearman ρ=0.369 and Accuracy=0.487 over this set. Overall, our findings underscore the need for AI designs that dynamically tailor empathic behaviors to user contexts and goals, offering a roadmap for future research and practical development of socially attuned, human-centered artificial agents.